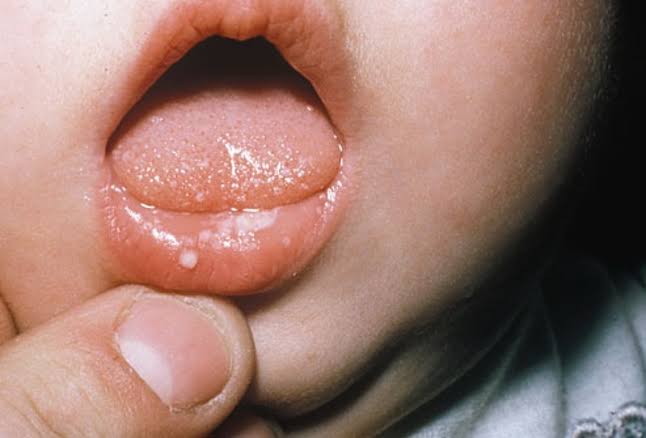
Chicken Pox in Pediatric age:
Causative Organism: Varicella Zoster virus
Mode of Transmission: Droplet spread, direct contact
Incubation Period: 14 to 16 days
Period of Infectivity: 7 days before onset of rash and 6 days after the development of rashes.

Chicken Pox in Pediatric age
Clinical Features of Chicken Pox in Pediatric age:
1. Prodromal Stage: Mild to moder- ate fever for 1 day associated with sore throat, headache, malaise.
2. Stage of Eruption: Rash appears within 24 hours from the onset of fever. It appears in crops. First appears on back then chest, abdomen, face and limbs.
Characteristics of Chicken Pox Rash
1. Polymorphic Rash: Macule, Papule and Vesicle.
All these 3 stages are present at a time. This helps in diagnosis of chicken pox on first day of fever.
2. Centripetal Distribution: Rash is more on limbs. Distribution starts from trunk and spreads towards limbs.
3. Conversion of macule to papule and papule to vesicle is rapid.
4. The vesicles are unilocular and can be ruptured easily. Vesicles are surrounded with erythematous margin. Some of the vesicles may turn into pustules (Pus formation in vesicles). The vesicles dry up in 2 to 5 days leaving behind scab which falls down leaving behind superficial scars.
5. Lesions may appear in mouth, conjunctiva, cornea and genital mucous membrane Other Associated Features of chicken pox in pediatrucv
1. Severe itching all over body
2. Lymphadenopathy: Mainly posterior cervical lymphadenopathy
3. Fever is intermittent and rises during appearance of new crop.
Complications of Chicken pox in Pediatric age:
1. Secondary infection of skin: Giving rise to furunculosis, cellulitis
2. Pneumonia
3. Encephalitis
4. Thrombocytopenia
5. If mother is having chicken pox during pregnancy congenital defect like atrophied limbs, microcephaly and retinopathy can occur in newborn baby.
Differential Diagnosis of chicken pox in Pediatric age
1. Impetigo: Mainly on face, maculo-papular rash with crust formation
2. Urticaria: Papules mainly on trunk, face is spared
3. Infected Scabies: Lesions mainly in webs of fingers
4. Insect bite allergy: Maculopapular vesicular rash mainly on exposed part of body
5. Herpes zoster. Multiple small vesi- cles along the nerve root
Treatment of Chicken Pox in pediatric age
1. Bed rest: For older children. Ab- stinence from school till the rash subsides.
2. For Fever: Syr. Paracetamol 30 to 40 mg/kg/day in divided doses
3. For severe itching: Antihistaminic drug: Chlorpheniramine maleate 0.35 mg/kg/ day in divided doses. Calamine lotion may be applied over the rash.
4. Treatment of secondary infection of skin: Syr. Erythrocin 30 to 50 mg/kg/day in divided doses. Syr. Cephalosporin or Amoxycillin can also be used.
Prevention from chicken pox in pediatric age
Varicella vaccine (Varilrix): Live attenuated vaccine. Dose- From the age of 12 months up to 12 years single dose of 0.5 ml subcutaneously. Booster dose is given between 4 to 5 years,
If someone is suffering from chicken pox in family then it hs completely compulsory to keep distance from others and that petson has to kept near clean and hygienic place with some amount of Neem leafs near him.
NOTE-Do not follow any (TOPIC:CONVULSIONS IN KIDS) treatment And medicine provided here ,please consult nearest hospital and talk to your doctor.This artical is only for knowledge purpose,consult your pediatric doctor for better support and follow the doctors medicine and WHO(WORLD HEALTH ORGANISATION) guide line for pediatric cases and about child health.
MOTHER CAN NOTE DOWN CHILD,S ROUTINE IN DIARY, TO HELP DOCTOR FOR BETTER TREATMENT AND UNDERSTANDING THE CHILDS PHYSIOLOGY AND ROUTINE ,SO THEY CAN PROVIDE BETTER TREATMENT AND USE BETTER MEDICINE FOR THAT CASE .
Ayurvedic medicine and its way of treatment can also be helpfull as you have to consult pediatric doctor(BALROG CHIKITSK)
Team-Dailyayurvedic
Thank you