TYPHOID FEVER IN KIDS-
Typhoid fever in kids is common in urban area due to poor sanitation and personal hygiene. During first few days of disease there is hardly any sign or investigation which can prove the diagnosis. For any fever lasting for more than one week, possibility of typhoid fever and primary complex should be kept in mind and patient should be investigated accordingly.
Causative Organisms of Typhoid fever in kids
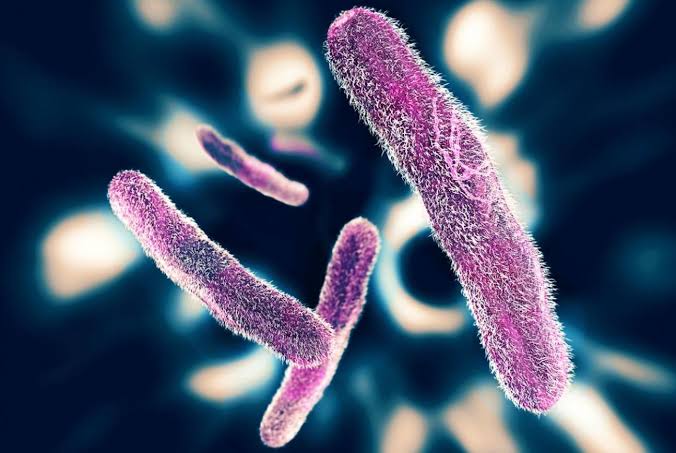
Salmonella typhi bacteria are causative organism. S. Paratyphi A and S. Paratyphi B are the other two organisms which can produce disease like typhoid fever but course of disease is milder. Treatment of disease caused by all these organisms is same.

Typhoid fever in kids
YOU CAN ALSO READ= https://medium.com
Mode of Transmission of Typhoid fever in kids
Infection is transmitted by ingestion of infected food, milk or water. Bacilli are excreted in stool and urine.
Incubation Period: Typhoid fever in kids
It varies from 7 to 21 days, average being 14 days.
Clinical Features forTyphoid fever in kids
It is less common in children below two years. If it occurs the clinical presentation is also different than that of older children. It presents with high fever, vomiting, loose motion and abdominal distension. In severe cases convulsions can also occur.
In older children, following features may be present.
1. Stage of Invasion (1st week)
(a.) Fever:
High fever with step ladder rise of temperature. Temperature is higher in the evening. Remittent fever is uncommon in children. It may be associated with shivering.
b. Gastrointestinal Symptoms:
Distension of abdomen, vom- iting and loose motion. Consti- pation may be found in some children. There might be local- ized tenderness mainly in right iliac fossa with tympanic note all over abdomen.
Cough, epistaxis may occur in some cases.
d. Associated symptoms like loss of appetite, bodyache, and headache. Tongue is coated in the center with clear margins (Typhoid ‘V’ tongue). If patient is treated with ap- propriate drugs at this stage, recovery starts without pro- ducing classical picture of typhoid. Untreated cases will proceed in stage of advance.
2. Stage of Advance (11nd week)
a. Fever remains high with slight remission in the morning. Patient may be toxic.
b. Loose motion and pain in abdomen continues. Spleen is enlarged.
c.Rose Spots: Usually occur C. from 7th to 10th day of fever. Reddish papules 2 to 5 mm in diameter and 10 to 20 in number, mainly on lower part of chest and abdomen. They disappear after 2 to 3 days.
3. Stage of Decline (3rd week)
(a)Fever: Starts coming down, a. toxemia decreases.
( b). Complications like intestinal hemorrhage, perforation, en- cephalopathy may occur in this stage.
4. Stage of Convalescence In untreated cases recovery takes 4 weeks.
Complications in Typhoid fever in kids-
1. Meteorism: Abdominal distension, tympanitis
2. Parotiditis: May occur due to oral sepsis and poor oral hygiene.
3. Hemorrhage: Streaks of blood or frank bright blood in stools
4. Intestinal perforation with signs of acute abdomen
5. Acute cholecystitis
6. Typhoid pneumonia: Common during 2nd week of illness
7. Encephalitis, meningitis, peripheral neuritis
8. Myocarditis
9. Arthritis, Osteomyelitis
10. Hemolytic Anemia
11. Alopecia
Investigations
Investigations done during first week may not lead to diagnosis since, test is positive only after 7th to 10th day of the disease, Drugs acting against typhoid are used during this period without proper diagnosis, may alter the response to widal test
1. Hb, CBC
a. Normochromic, normocytic anemia.
b. Leukopenia: WBC count may be as low as 3000/mm3.
c. Thrombocytopenia.
2. Urine Examination:
Urine Albu- min present in trace.
3. Widal test
Titre of S. Typhi ‘O’ more than 1:80, it is diagnostic. S. Typhi-H and S. Paratyphi-A and B can be raised in the patients who are previously inoculated (anamnestic reaction). Similarly, treatment with antityphoid drugs also changes the titre pattern.
Limitations of Widal Test in Diagnosis of Typhoid
1. It takes minimum 7 to 10 days to get positive widal test.
2. Treatment with antityphoid drug during this period will again change the titre.
3. Cough, vomiting diarrhea may be considered as symptoms of other systemic diseases and they can be treated with drugs like Ampicillin, Chlorampheni- col, Co-trimoxazole which will alter the result of widal test.
4. Though rising titre of ‘0’ antigen is diagnostic, it is not practical to repeat the examination of blood.
5. S. Typhi H and S. Paratyphi A and B may be +ve in previously inoculated patient.
6. Negative widal test does not rule out typhoid.
4. Blood Culture
This is done to prove the diagnosis of typhoid. It is found +ve in 80% of cases during 1st week.
5. Stool Examination
This may show plenty of pus cells (leucocytes), RBCS and occult blood may be present in stool.
Treatment of Tyohoid fever in kids
1. Chloramphenicol still remains the drug of first choice. But injudicious use of chloramphenicol in other conditions and administration of subtherapeutic dose has led to development of drug resistance. Therefore, one should establish the diagnosis with laboratory in- vestigations and then start chlor- amphenicol in proper dosage and duration.
Dosage in kids for Typhoid fever in kids
In infants Syr. Chloramphenicol 25 mg/kg/day in divided doses. Injectable chloramphenicol can be used in severe cases.
In older children 50 mg/kg/day in divided doses.The treatment should be continued at least for 10 to 14 days or 5 to 7 days following complete recovery. Use of Chloramphenicol is on decline because of its side effects like blood dyscrasias. Other safe drugs are more preferred.
2. Other drugs which can be used are, Amoxycillin 30-40 mg/kg/day, Ampicillin 100-200 mg/kg/day OR Cefixime or Cefpodoxime 8 mg/ kg/day OR Inj. Taxim OR Co-trimoxazole- 8 to 10 mg/kg of trimethoprim in 2 divided doses OR Furazolidone 8 to 10 mg/kg in 3 divided doses.
3. Nowadays many pediatric typhoid cases are treated with Norfloxacin or Ciprofloxacin. Dose- Norfloxacin: 10 to 15 mg/ kg/day orally in 2 divided doses 7 days. Dose- Ciprofloxacin: IV 5 to 10 mg/ kg/day in 2 divided doses. Oral dose 10 to 15 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses x 7 days.
Supportive Treatment for Typhoid fever in kids-
1. Syr. Paracetamol 30 to 40 mg/kg/ day for symptomatic relief from fever.
2. Maintenance of oral hygiene.
3. Diet: Patient can have routine diet except for oily and spicy food items.
4. If severe vomiting persists, patient should be kept on maintenance IV fluids.
5. In patient with severe toxemia and circulatory failure,corticosteroid is used with caution.
NOTE- Do not follow any treatment And medicine provided here ,please consult nearest hospital and talk to your doctor.This artical us only for knowledge purpose.
Team-Dailyayurvedic
Thank you